Author: Dr. Oreste Di Mattei Di Matteo
Date: 20/01/2020
What are the methods for removing tattoos?
Many surgeons claim that complete removal of a tattoo is impossible. What techniques can be used in removing tattoos or making them less visible? There are different methods, each with a different effectiveness and taking different times. The following variables always condition the success of tattoo removal:
- Size
- Position
- Age of tattoo
- Colours and type of ink used
Only a surgeon experienced in removing tattoos can help achieve the desired results.
Tattoo removal techniquesThe most common methods for tattoo removal include:
- Removal of the skin where the tattoo was performed
- Dermabrasion
- Laser
- Chemical peels
Removal Removal or excision involves a real removal of the tattooed skin. This technique is generally used only on small tattoos or small parts of a tattoo, which can be removed a little at a time. This method leaves a scar.
Dermabrasion Dermabrasion work thanks to abrasion of the skin and then of the tattoo. There may be bleeding of the part during treatment. This procedure is performed under local or local and oral anaesthesia and under sedation.
Chemical peelsA chemical is used in a chemical peel, usually an acid solution that causes skin exfoliation.
The chemical solution is based on trichloroacetic acid (TCA), a peel medium.
During the procedure, a burning sensation is felt, followed by a feeling of numbness or tingling.
After the procedure with TCA there may be some swelling of the part. You should always contact a doctor for applications, because the do-it-yourself approach could cause serious damage to the skin in the long term.
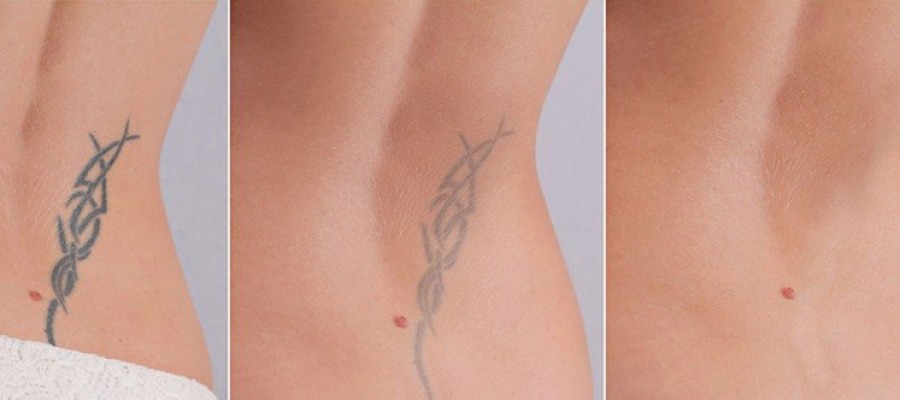
Laser The laser causes breakdown of the ink pigments injected into the skin. The laser dissolves the colour particles, which are then eliminated from the body as metabolic waste. If you follow the path of tattoo removal using a laser, you should be aware that it takes at least 2 years to remove a tattoo, and the process is not completely guaranteed. Times and results depend entirely on:
- Type of laser
- Number of sessions
- Individual response to treatment
Tattoo removal: when it is not recommendedIt is not recommended undergoing tattoo removal in the presence of:
- keloids
- hyper- or hypopigmentation
- There is no good individual response to the healing of burns
- It is predisposed to the formation of scars also for small traumas
Why is it not recommended undergoing tattoo removal if these problems occur?
Surgical and laser methods could cause more evident scars in the post-treatment phase.
Chemical peels should only be done in a doctor's surgery because they could seriously damage the skin if subject to these problems.
Dermabrasion. If the abrasions heal badly, the results of dermabrasion could be disastrous. Furthermore, if you are prone to hyper- or hypopigmentation, dermabrasion is not recommended.
Lasers may cause burns, so if they do not heal well this could be a problem.
Post-treatment infections or irreversible damage to the skin may occur.
Tattoo removal: Colours It is difficult to predict whether tattoos will fade or be resistant to treatment because there are hundreds of inks for each colour used in creating tattoos. In some cases there are inks that do not seem to respond to treatment, especially laser treatment. Tattoo removal is possible, but it depends greatly on the colour and type of ink used. The doctor experienced in tattoo removal will be able to recommend the most appropriate treatment, evaluate the range of colours in the tattoo and suggest the degree of success of the treatment.
After tattoo removal treatment The skin will need to be treated with care for 1 to 2 weeks after each treatment.
It is necessary to use sun protection during treatment.
What are the side effects?
The side effects are scars and pain in general.
Tattoo removal: some suggestions To undergo tattoo removal you must be in good psycho-physical condition because it requires much patience and a good emotional balance.